
Introduction
The financial world is undergoing a transformative shift as decentralised finance (DeFi) and traditional finance (TradFi) converge, paving the way for a promising future. With DeFi’s innovative approach backed by blockchain technology, and TradFi’s deep-rooted experience and stability, the amalgamation of these two spheres offers unparalleled opportunities for investors and financial institutions alike. DeFi is revolutionising the sector by eliminating intermediaries, empowering individuals to have greater control over their assets, and enabling seamless cross-border transactions. While TradFi brings years of industry knowledge and established regulations, fostering trust and mitigating risks. Both worlds, though distinct, have distinct advantages that, when combined, can shape a more inclusive and efficient financial ecosystem. This article explores the convergence of DeFi and TradFi, highlighting the significant advancements and potential challenges, ultimately demonstrating the importance of embracing this transformative union to unlock the full potential of the financial sector.
Companies that neglect to invest in and embrace new technologies may find themselves falling behind, losing market share, and facing challenges in the increasingly dynamic and globalised marketplace.
Defining Decentralised Finance (DeFi’s) and Traditional Finance (TradFi’s)
The concept underlying decentralized finance (DeFi) is the possibility of reconstructing the conventional financial system utilizing blockchain technology. The objective is not to enhance the current establishments, but rather to supplant convoluted bureaucratic procedures and ineffective processes with intelligent contracts and tokenomics.
Figure 1: The premise behind Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Source: Consensys
As for Traditional Finance (TradFi’s) conventional financial institutions adhere to a centralized model, wherein all customers are obligated to engage with a bank or exchange. These intermediaries validate and facilitate transactions, and additionally act as custodians for assets.
On the contrary, within a decentralized network, transactions occur directly between individuals (peer-to-peer or P2P), and assets are stored in a fragmented manner across numerous computers or nodes which are rented out privately.
The absence of intermediaries results in various advantages, namely: 1) reduced costs and 2) enhanced transactional speeds. Moreover, the decentralized system also boasts increased reliability, as it effectively eliminates the potential for human error (at least in theory). Furthermore, this system is less biased, as services provided are equally accessible to all individuals. 1
However, the primary objectives of the conventional financial system as a whole (including banks, other financial institutions, and investors) are to facilitate effective capital allocation decisions and provide funding for productive endeavors. This productivity refers to financing growth through the creation of jobs and investments, with an emphasis on profitability and sustainability. 2
From Evolution to Revolution: Understanding the Unprecedented Speed of Disruption
When it comes to the disruption of long-established companies by fast-moving, tech-enabled powerhouses, the clash between decentralized finance (DeFi) and traditional finance (TradFi) takes center stage. Older companies often face not a lack of inspiration, but rather an excess of institutional control and an inability to scale up innovations. This is evident in a recent McKinsey survey, where many respondents highlighted how parent companies have hindered the development of their start-ups and restricted entrepreneurs’ freedom to make crucial decisions. In fact, McKinsey forecasts that by 2027, approximately 27% of the companies currently listed on the S&P 500 will cease to exist.
As indicated by Coingecko’s data, the market capitalization of the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector has reached an impressive $52 billion in 2023. This figure is expected to rise even more due to the increasing adoption of DeFi-related services and ongoing trends.
The upcoming year is expected to witness significant advancements and emerging technologies in the DeFi space that have the potential to revolutionize the financial sector. These developments encompass cross-chain integrations, heightened security measures, increased institutional adoption, expansion of use cases across diverse industries, and the evolution of governance models within DeFi projects. 3
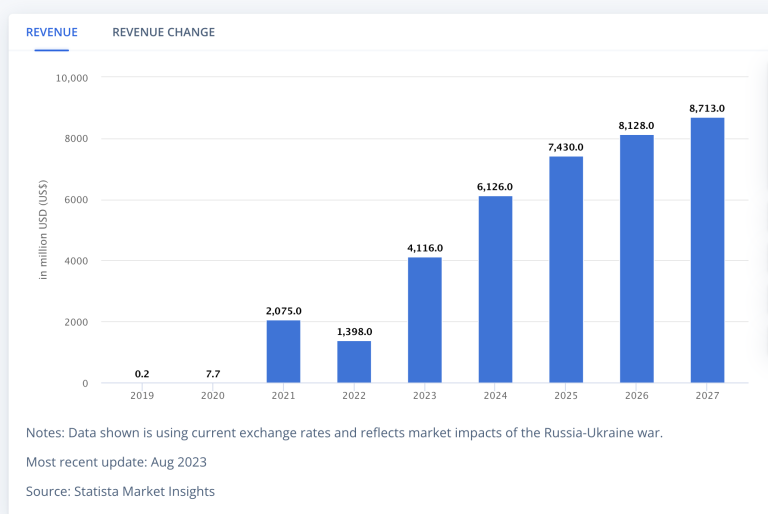
Figure 2: DeFi Europe – Source Statista
Navigating the TradFi Minefield: Understanding its Pitfalls in the Modern Financial Sphere
In the wake of the collapse of the financial sector, central banks around the globe have been compelled to prioritize stability, recovery, and growth. Presently, the sector encounters numerous challenges related to financial inclusion and digitization. It is crucial to contemplate alternative approaches at this juncture in order to promote financial freedom and enhance prospects for a sounder financial future.
The TradFi ecosystem is overseen by various centralized entities that are bound by stringent regulations. These regulations pose significant obstacles for TradFi institutions in embracing change, making it exceedingly challenging, if not unfeasible. Moreover, operating TradFi organizations entails considerable expenses. Implementing wide-ranging alterations inherently carries risks, as it incurs numerous costs and may not yield an immediate return on investment.
The legal foundation of central banks, such as the Federal Reserve System, extends back several decades, if not centuries. While laws are occasionally amended, they typically refine the existing system rather than effect wholesale transformations. For instance, many of the amendments to the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 primarily aim to grant the Fed greater authority over the TradFi ecosystem in the United States.
Traditional financial (TradFi) institutions frequently exhibit reluctance when it comes to embracing emerging technologies. They face the need to adhere to stringent regulations, obtain consent from board members, and make substantial investments before incorporating new technologies into their operations.
In the realm of TradFi, transaction costs tend to be exorbitant. Banks, brokers, and other such entities aim to generate profit from transactions. Conversely, decentralized finance (DeFi) systems often automate numerous roles, resulting in reduced overall costs.
Here are some benefits of TradFi’s:
- Regulatory Framwork
- Market Maturity and Stability
- Liquidity
- Risk Management Tools
- Established Infrastructure
- Expertise and Professional Advice
- Credit Borrowing Facilities
- Investment Diversification
- Insurance and Protection
- Government Support and Backing
Riding the Wave of Financial Innovation: How DeFi is Revolutionizing the Way We Transact and Invest
The phenomenon of DeFi, has emerged as a prominent trend within the cryptocurrency industry in recent years, and its evolution is expected to persist in the forthcoming years of 2024 and beyond. DeFi possesses the capability to revolutionize conventional financial systems by offering decentralized lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming platforms. As the DeFi ecosystem proceeds towards reaching maturity, it is plausible to anticipate the emergence of more sophisticated financial products and enhanced interoperability among DeFi protocols, which will grant users a more diverse range of opportunities and greater accessibility to a wider spectrum of financial services.
The traditional finance (TradFi) ecosystem operates with a deliberate pace, emphasizing stability and established practices. However, the emergence of disruptive technologies such as blockchain has compelled numerous TradFi organizations to explore alternative avenues.
Gradually, TradFi institutions are recognizing the multitude of advantages offered by recent technological breakthroughs. Notably, the Federal Reserve has openly acknowledged its investigation of a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), which shares similarities with a stablecoin.
The aforementioned institutions are gradually transitioning towards establishing a financial system that encompasses DeFi. Esteemed FinTech entities like CashApp and Robinhood have already begun providing crypto assets. Prominent Traditional Financial institutions, including the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston, have acknowledged their exploratory pursuits regarding the coexistence of DeFi and TradFi. However, the implementation of these integrations is not expected to occur imminently, as the potential risks associated with them are still undergoing assessment. 4
Many other companies that embody the coexistence of Traditional Finance (TradFi) and Decentralised Finance (DeFi) often operate in various sectors, offering services that integrate both traditional and decentralized financial elements such as Binance, Coinbase, Blockfi, Aave and many more.
Here are some of DeFi’s benefits:
- Accessibility and Inclusivity
- Financial Inclusion
- Transparency
- Lower barriers to entry
- Interoperability
- 24/7 Accessibility
- Programmabilty and Smart Contracts
- Yield Opportunities
- Reduced Counterparty Risks
- Innovation and Experimentation
Conclusion
One of the key advantages of the convergence between traditional finance (TradFi) and decentralized finance (DeFi) lies in its potential to extend financial services to individuals who were previously excluded from or had limited access to banking services. The decentralized structure of DeFi empowers individuals to directly avail themselves of financial services, bypassing intermediaries like banks. This fosters greater financial inclusion, particularly for those living in underdeveloped nations with limited or no access to conventional banking services.
Furthermore, by catering DeFi products to their clients, centralized exchanges can provide a robust and compliant infrastructure reminiscent of traditional finance (TradFi) while also offering a vast array of decentralized offerings. Consequently, numerous individuals who have been unable to partake in the secure and regulated realm of the DeFi market may now have the opportunity.
Regulatory, compliance, and consumer protection are crucial aspects for the sustained growth and stability of the DeFi space.
The convergence of traditional finance (TradFi) and decentralized finance (DeFi) can serve as a means to establish a more comprehensive financial ecosystem that caters to diverse individuals. By combining the strengths of both systems, TradFi can furnish the necessary security measures and regulatory framework that DeFi currently lacks. Conversely, DeFi can present a decentralized and inclusive financial platform, exceeding the capabilities of its conventional counterpart.
For instance, Islamic Coin is facilitating the inclusion of investors from the global Islamic community into the cryptocurrency economy by offering them an asset on the Haqq blockchain ecosystem that prioritizes ethical considerations and complies with Shariah law. Its token supply is limited, ensuring that it fulfills all the requirements of a Halal asset, which is built upon the principles of sustainability, ethics, and transparency. Furthermore, all financial information pertaining to this project, such as transactions, can be conveniently accessed online through Gnosis Safe.
An equally noteworthy initiative in this domain is Circle, a technology company focused on peer-to-peer payments. It aims to bridge the gap between decentralized finance (DeFi) and traditional finance (TradFi) by harnessing the potential of blockchain technology. Circle enables individuals to make global money transfers using USDC, a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. With just a simple click, individuals can leverage the advantages offered by both technological spaces. 5
The relationship between DeFi and TradFi will likely involve a balance between competition and collaboration, driven by shared goal of improving financial services and expanding access for users worldwide.
Sources:
- Defining Decentralized Finance (DeFi) & Traditional Finance (TradFi’s) – https://rossdawson.com/futurist/companies-creating-future/defi-companies-future-decentralized-finance/
- Decentralised Finance: Good technology bad finance – https://www.bruegel.org/policy-brief/decentralised-finance-good-technology-bad-finance
- Crypto Trends in 2024: https://weissratings.com/en/weiss-crypto-daily/4-crypto-trends-to-keep-on-your-2024-radar
- Future of TradFi: https://hedera.com/learning/decentralized-finance/tradfi
- Merging of TradFi and DeFi: https://www.financemagnates.com/fintech/merging-of-tradfi-defi-the-best-of-two-worlds/
Contact us

Stuart Thomson
Partner,
Aspect Advisory
![]()
